Navigating the High-Stakes World of Restaurant Turnarounds
Restaurant turnarounds are critical in an industry where downturns can strike suddenly, turning once-thriving establishments into struggling operations. Whether it’s due to external economic factors, internal mismanagement, or shifting consumer preferences, the need for a strategic turnaround becomes critical. For middle-market and upper-middle-market investors, the stakes are particularly high. When performance falters, swift and strategic action can be the difference between recovery and collapse.
At Aaron Allen & Associates, we’ve led numerous successful turnarounds, leveraging decades of industry expertise to guide businesses back to profitability. This comprehensive guide dissects the anatomy of a successful restaurant turnaround, enriched with real-world case studies that illustrate how various strategies have been applied in different contexts.
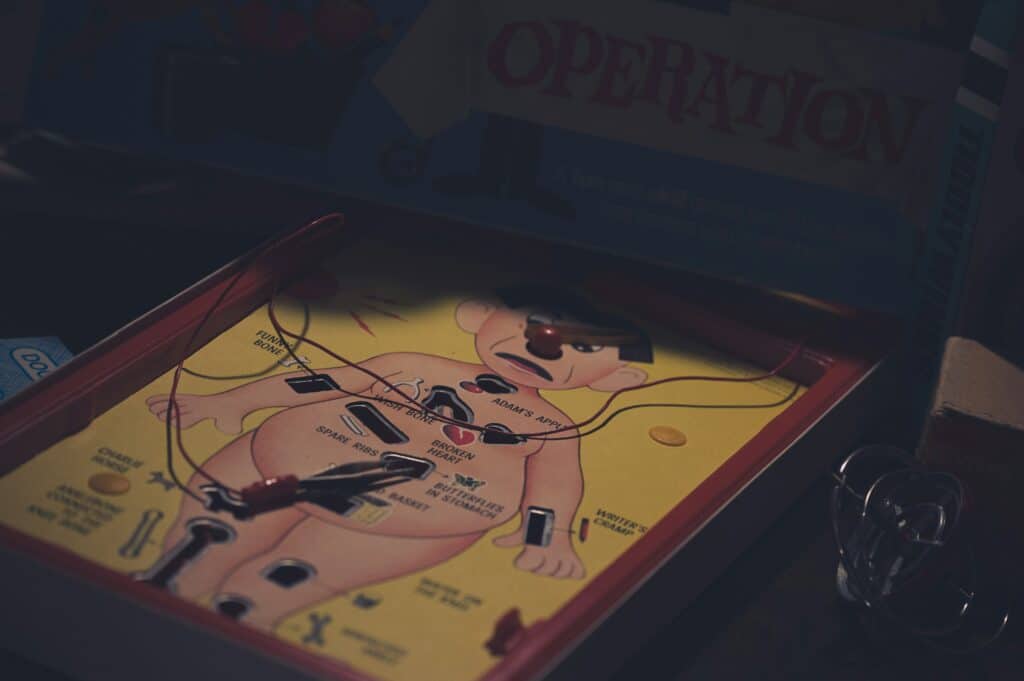

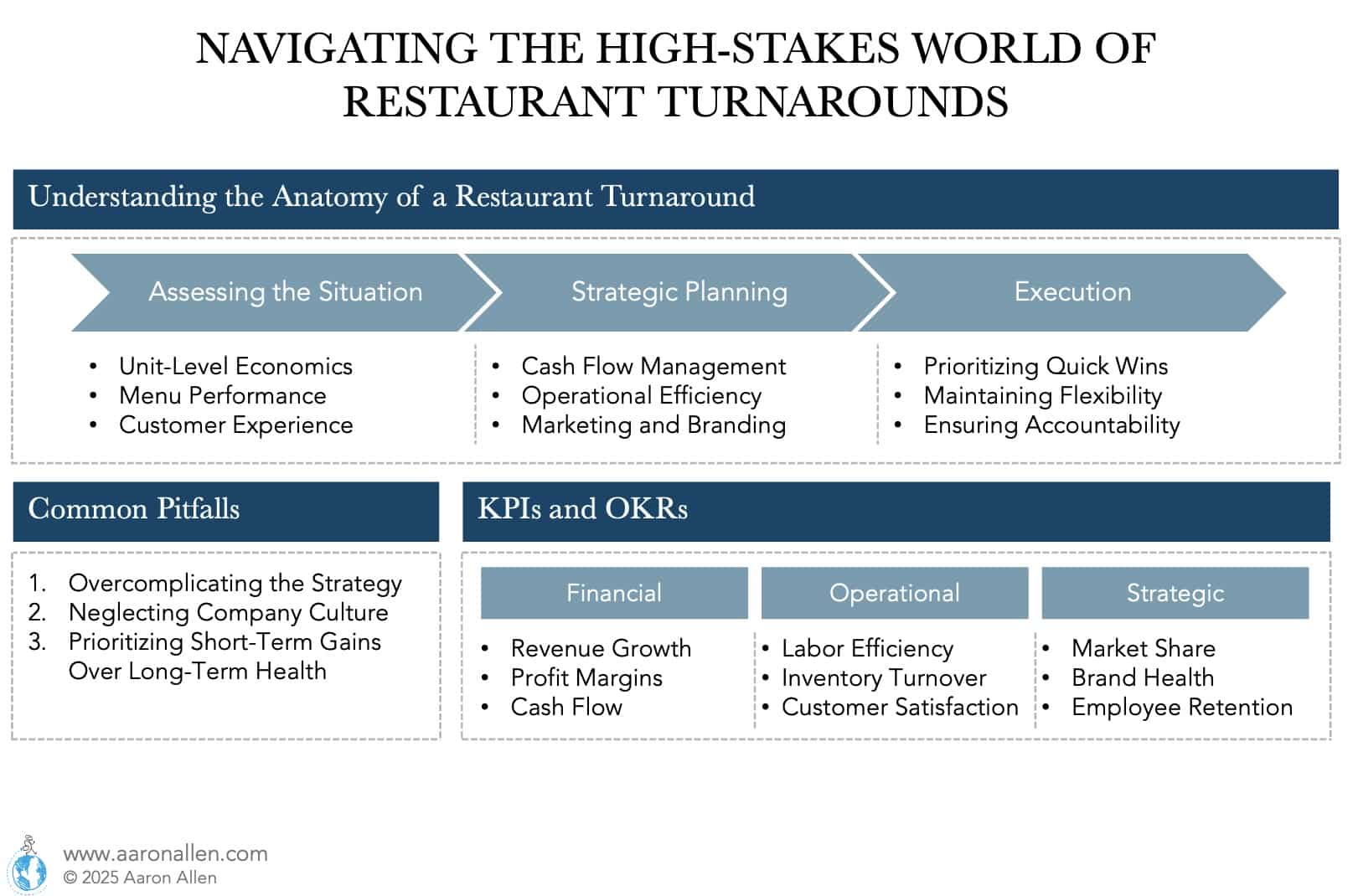
Understanding the Anatomy of a Restaurant Turnaround
A restaurant turnaround is a multifaceted process requiring a blend of financial acumen, operational expertise, and strategic marketing. It’s an even more complex process if it involves a chain rather than an independent restaurant. Let’s explore the critical steps involved, supplemented with diverse case studies and practical insights.
1. Assessing the Situation: The Foundation of Recovery
The first step in any successful turnaround is a thorough assessment of the current state of the business. This involves diving deep into financials, operational data, customer feedback, and market conditions. Key areas of focus include:
- Unit-Level Economics: Understanding the profitability of each location is critical. For example, Wendy’s employed a strategy of closing or restructuring underperforming locations, which was essential in their turnaround efforts during the 2010s.
- Menu Performance: Identifying high-margin items and eliminating those that drain resources is vital. Pizza Hut, during its early 2010s turnaround, streamlined its menu to focus on core offerings, boosting profitability.
- Customer Experience: Gathering and analyzing customer feedback helps pinpoint areas for improvement. After its food safety crisis, Chipotle focused on restoring customer trust through enhanced food safety measures and a renewed emphasis on quality, which played a crucial role in its recovery.
2. Strategic Planning: Crafting a Roadmap for Success
With a clear understanding of the issues at hand, the next step is to develop a comprehensive turnaround plan. This plan should address all critical aspects of the business, including:
- Cash Flow Management: Stabilizing cash flow is often the first priority. For instance, Burger King’s turnaround under 3G Capital involved aggressive cost-cutting measures and a focus on improving cash flow by reducing unnecessary expenses.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlining operations to reduce waste and improve productivity is essential. Arby’s revitalization during the mid-2010s is a prime example, where the brand focused on operational efficiencies and rebranding to reconnect with its core audience.
- Marketing and Branding: Repositioning the brand to attract customers and improve market share is a key component of any turnaround. Nando’s, for example, leveraged its South African roots and vibrant brand personality to expand globally, repositioning itself as a leader in the casual dining space.
3. Execution: Bringing the Plan to Life
Executing the turnaround plan requires disciplined implementation and continuous monitoring. Key strategies include:
- Prioritizing Quick Wins: Focus on actions that can deliver immediate results. KFC, during its recent turnaround, introduced innovative marketing campaigns and menu offerings that quickly resonated with consumers, driving a swift recovery in sales.
- Maintaining Flexibility: Adapt strategies as new challenges or opportunities arise. Domino’s Pizza’s “Pizza Turnaround” campaign in 2009 is a classic example, where the company overhauled its product and marketing strategy in response to customer feedback, leading to a significant rebound.
- Ensuring Accountability: Assigning clear roles and responsibilities is critical to maintaining alignment and ensuring successful execution. Ford Motor Company’s turnaround under Alan Mulally demonstrated the importance of transparency and accountability.
Start a Transformation
The Role of External Advisors: When to Seek Expert Help
External advisors, like Aaron Allen & Associates, can provide critical support. Bringing in an outsider’s perspective can help identify blind spots and accelerate the recovery process.
- Board/Investor Concerns: If the board or current investors think the existing team lacks experience in turnarounds or is resistant to change, external advisors can provide fresh insights and drive necessary transformations.
- Rapid Decline: When a business is in free fall, immediate and decisive action is needed. Chrysler’s turnaround, led by Lee Iacocca, involved rapid intervention to stabilize the company’s finances and operations.
- Complex Challenges: Multifaceted issues, such as those faced by Starbucks in the coffee category during its late 2000s turnaround, require specialized expertise. External advisors can help navigate these complexities, ensuring that all aspects of the business are addressed while the CEO is too busy with the day-to-day.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls in Restaurant Turnarounds
Restaurant bankruptcies are increasing and even with a well-crafted plan, turnarounds can fail if common pitfalls are not managed carefully. Here are some mistakes to avoid:
- Overcomplicating the Strategy
A complicated strategy can lead to confusion and poor execution. Simplify the plan where possible and focus on clear, actionable steps. Denny’s faced this challenge during its 1990s turnaround and learned that a streamlined, focused approach was more effective.
- Neglecting Company Culture
Cultural change is often necessary during a turnaround. Engaging employees, communicating openly, and maintaining morale are crucial. Pret A Manger’s expansion strategy emphasized maintaining a positive workplace culture, which was essential to its success.
- Prioritizing Short-Term Gains Over Long-Term Health
While quick wins are important, they shouldn’t come at the expense of the business’s long-term viability. Balancing short-term actions with strategies for sustainable growth is key, as demonstrated by Tim Hortons during its U.S. expansion.
Take Action Today
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Objectives and Key Results (OKRs)
To track progress and measure success, it’s essential to establish and monitor the right KPIs and OKRs. These metrics provide a clear view of how the turnaround is progressing and where adjustments may be needed.
- Financial Metrics
- Revenue Growth: Monitoring sales performance is crucial to ensure the turnaround is on track. McDonald’s “Plan to Win” strategy, implemented in the early 2000s, focused heavily on driving revenue growth through operational improvements and menu innovation.
- Profit Margins: Keeping a close eye on profit margins helps identify areas where cost control efforts are working. Popeyes saw significant margin improvements following its operational overhaul, which included menu optimization and streamlined operations.
- Cash Flow: Ensuring positive cash flow is fundamental to supporting ongoing operations and investments in the business. Ford’s turnaround focused on improving cash flow through a combination of cost-cutting and strategic investments.
- Operational Metrics
- Labor Efficiency: Assessing labor costs relative to revenue helps identify opportunities for optimization. Sonic Drive-In focused on improving labor efficiency through the integration of technology, which played a key role in its operational turnaround.
- Inventory Turnover: Tracking inventory levels and turnover rates is essential for reducing waste and optimizing costs. YO! Sushi’s global expansion strategy involved meticulous inventory management to ensure profitability across diverse markets.
- Customer Satisfaction: Regularly measuring customer satisfaction through surveys and reviews provides insights into how well the turnaround is resonating with consumers. Chick-fil-A’s focus on customer service excellence has been a cornerstone of its success, consistently driving high customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Strategic Metrics
- Market Share: Monitoring market share helps assess the competitive position of the business. Starbucks’ turnaround strategy in the late 2000s included efforts to regain market share through product innovation and enhanced customer experiences.
- Brand Health: Tracking brand perception through social media engagement and customer feedback is crucial for understanding the impact of turnaround efforts. Taco Bell’s revitalization strategy involved significant investments in brand health, resulting in a strong rebound in market presence.
- Employee Retention: Keeping track of turnover rates and employee satisfaction levels ensures that key staff remain engaged and motivated. Panera Bread’s digital transformation included efforts to improve employee retention, which was critical to maintaining service quality during the transition.
Measuring Success: The Timeline and Cost of a Turnaround
A restaurant turnaround is not an overnight process. It typically takes 12 to 24 months to see substantial results, although early improvements may be visible within the first few months. The cost of a turnaround can vary based on the size and complexity of the business, but it generally includes consulting fees, operational investments, and marketing expenses. Proper budgeting and financial planning are crucial to ensure that the business has the resources it needs to achieve a successful turnaround.
Who Should Be Involved in the Turnaround?
A successful turnaround requires collaboration across multiple levels of the organization. Key stakeholders include:
- Leadership Team: The CEO, CFO, and other senior leaders must be actively involved in guiding the turnaround process. The leadership-driven turnarounds at companies like Ford under Alan Mulally and Apple under Steve Jobs highlight the importance of committed leadership in driving recovery.
- External Advisors: Specialized consultants bring expertise and objectivity, helping to navigate complex challenges and drive effective change. The involvement of turnaround specialists, as seen in several successful restaurant recoveries, can be the key to revitalizing a struggling business.
- Employees: Engaging frontline staff is critical to executing the turnaround plan and ensuring buy-in across the organization. Pret A Manger and Nando’s both emphasized employee engagement during their expansion and turnaround phases, recognizing that motivated employees are essential for delivering consistent customer experiences and sustaining long-term growth.
Restaurant Turnaround Case Studies
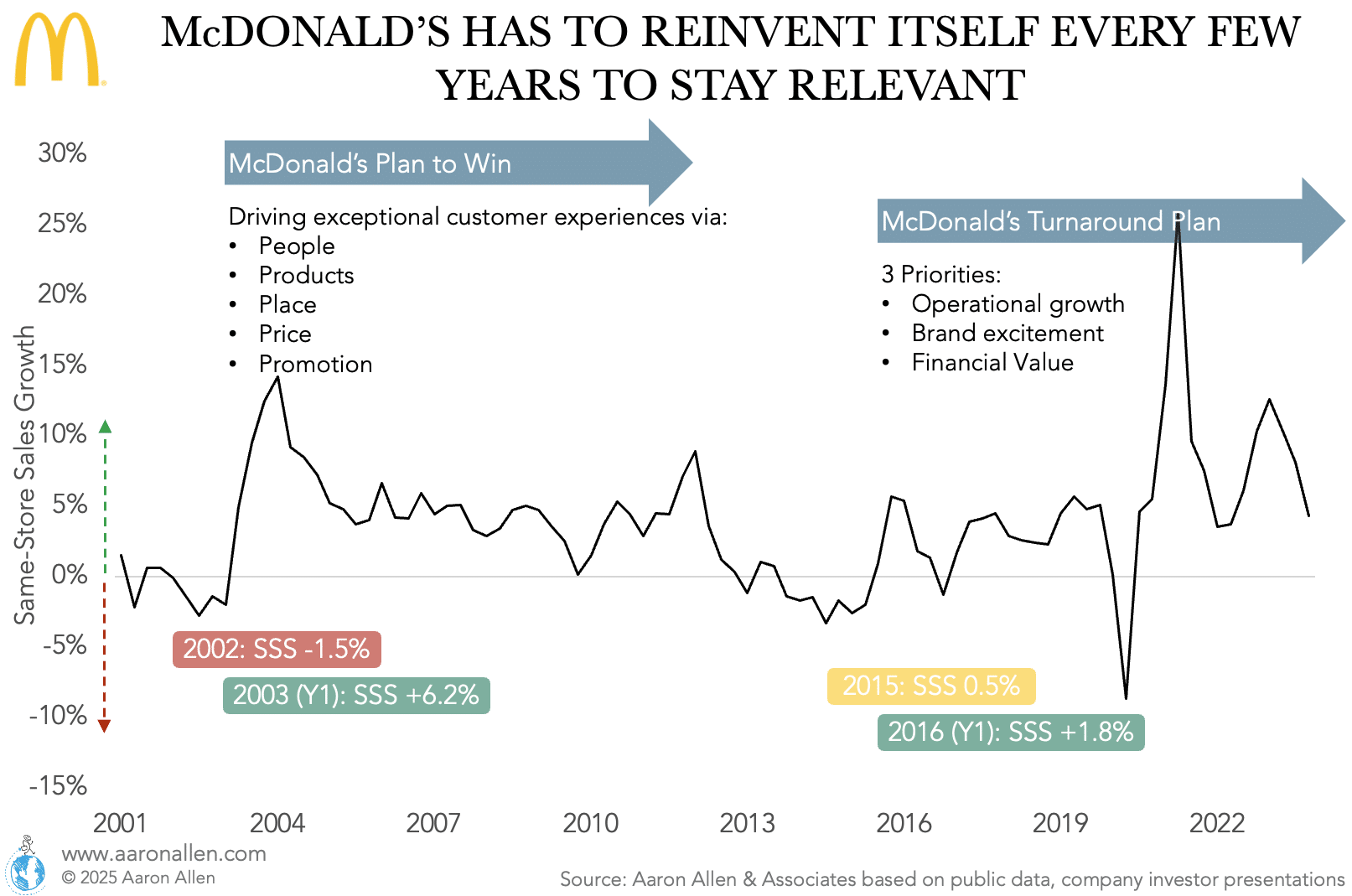
McDonald’s Long History of Turnarounds
McDonald’s has undergone several turnaround efforts throughout its history, each offering key insights into the anatomy of a successful corporate revitalization. Two significant examples are the “Plan to Win” strategy initiated in the early 2000s and the more recent efforts under CEO Steve Easterbrook beginning in 2015.
- McDonald’s Plan to Win (2003):
Under the leadership of Jim Skinner, McDonald’s launched the “Plan to Win” strategy in 2003. This initiative was in response to declining sales, growing competition, and a damaged brand image largely tied to concerns about unhealthy food. The strategy focused on improving McDonald’s core areas: quality, service, cleanliness, and value (QSCV). This was achieved through a combination of menu innovation, operational efficiencies, and a rebranding effort. McDonald’s introduced healthier menu items, improved the quality of its existing offerings, and rolled out the “Made for You” system, allowing for greater customization and freshness in orders. These efforts led to a significant rebound in the company’s fortunes, culminating in McDonald’s reporting its highest-ever quarterly profits by 2007 and a 50% increase in stock price.
Key Learnings:
- Menu Innovation: Introducing healthier options and improving existing products can effectively address changing consumer preferences.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlining operations to reduce waste and improve service quality is critical for enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Brand Repositioning: A focused marketing campaign to shift consumer perceptions can significantly enhance brand image and drive growth.
- McDonald’s Turnaround Plan (2015):
In 2015, McDonald’s was again facing challenges—declining same-store sales, a cluttered menu, and increasing competition from both traditional rivals and healthier fast-casual concepts. Steve Easterbrook, who became CEO in March 2015, implemented a comprehensive turnaround strategy. This included reorganizing the business into four distinct market segments based on market maturity, increasing franchisee ownership, simplifying the menu, and launching initiatives such as all-day breakfast and made-to-order burgers. While the strategy received mixed reactions, it represented a bold attempt to align McDonald’s operations with contemporary consumer expectations and improve operational efficiencies.
Key Learnings:
- Market Segmentation: Reorganizing business units to better address market maturity and consumer preferences can help focus strategic efforts more effectively.
- Franchisee Relations: Increasing franchisee ownership and simplifying operations can drive efficiencies but must be managed carefully to maintain service quality.
- Consumer-Centric Innovation: Offering new products or services that align with customer demands (e.g., all-day breakfast) can reinvigorate consumer interest and boost sales.
These case studies illustrate that successful turnarounds at McDonald’s have often hinged on a combination of operational efficiency, brand repositioning, and strategic innovation. The lessons from these efforts are valuable for any business looking to reverse a decline and reestablish growth.
Domino’s Compelling Turnaround Campaign
Domino’s Pizza provides a compelling case study on how a brand can successfully execute a turnaround, even when facing significant challenges. In the late 2000s, Domino’s was struggling with declining sales, poor customer perceptions of its product, and a damaging viral video scandal. The company’s pizza was often criticized as being bland and “tasting like cardboard,” with many consumers preferring even microwave pizza over Domino’s offerings.
The Turning Point: “Pizza Turnaround” Campaign (2009-2010):
The pivotal moment came when then-CEO Patrick Doyle and his team decided to confront the criticism head-on. They launched the “Pizza Turnaround” campaign in 2009, which was characterized by its brutally honest approach. The campaign featured real customer feedback that highlighted the brand’s shortcomings and showed the steps Domino’s was taking to improve. This included a complete overhaul of their pizza recipe—new crust, new sauce, new cheese—to address the quality concerns.
The honesty and transparency of this campaign resonated with consumers, and it marked the beginning of a significant recovery for Domino’s. In 2010, the company saw a 14.3% increase in revenue, and its stock price rose by 130%. Over the next decade, Domino’s continued to innovate, embracing technology with initiatives like the Pizza Tracker, online ordering, and mobile apps, which contributed to its rise as the largest pizza chain globally by sales.
Key Learnings from Domino’s Turnaround:
- Radical Transparency: Domino’s decision to publicly acknowledge its faults and commit to change played a crucial role in regaining customer trust.
- Product Overhaul: Addressing core product issues—like the taste of the pizza—ensured that the marketing campaign was backed by real, substantive changes.
- Integration of Technology: Embracing digital innovation allowed Domino’s to enhance customer convenience and stay ahead of the competition, with over 70% of their U.S. sales now coming from online orders.
- Effective PR and Marketing: The campaign’s integration of traditional advertising, PR, and social media helped create a unified message that resonated with a broad audience.
This case underscores the importance of listening to customers, being transparent, and aligning product improvements with marketing efforts. Domino’s not only recovered from its low point but emerged as a leader in the global pizza market, showcasing how a well-executed turnaround can deliver long-term success.
Improve Your Margins
Private Equity Firms Can Also Stir Restaurant Turnarounds
Burger King’s turnaround under the ownership of 3G Capital is a fascinating example of how disciplined strategy, cost control, and innovation can revive a struggling brand. By the late 2000s, Burger King was in trouble — facing declining sales, a revolving door of leadership, and poor execution compared to competitors like McDonald’s.
3G Capital’s Acquisition and Strategy: In 2010, 3G Capital acquired Burger King for $3.3 billion, setting the stage for a transformation. 3G implemented its hallmark strategies of zero-based budgeting, cost-cutting, and a relentless focus on efficiency. This included refranchising most of Burger King’s company-owned stores, which transferred capital expenditure burdens to franchisees, significantly boosting free cash flow. Additionally, the company streamlined general and administrative expenses, which improved operating leverage.
Leadership and Cultural Shifts: Daniel Schwartz, who became Burger King’s CFO shortly after the acquisition and then CEO in 2013, played a crucial role in this transformation. Schwartz brought a hands-on leadership style, even working shifts in Burger King restaurants to better understand the business. Under his leadership, the company returned to the public market in 2012 and focused on international expansion, marketing innovations, and operational improvements. By 2014, Burger King’s stock had doubled while McDonald’s experienced a decline.
Marketing Innovation: Burger King also made headlines with bold, unconventional marketing strategies that resonated with younger audiences. Campaigns like the “Whopper Detour,” which offered a Whopper for one cent if ordered near a McDonald’s, leveraged technology to create buzz and drive app downloads. Other campaigns, such as the “Proud Whopper” during LGBT Pride and the “OK Google” ad that interacted with home devices, showcased Burger King’s ability to blend creativity with brand messaging.
Results: The results of these efforts were impressive. Between 2015 and 2017, Burger King’s system-wide sales grew at an average compound rate of 9.4%, and the brand’s value more than doubled from $3.17 billion in 2015 to $6.56 billion in 2018. This turnaround not only revitalized Burger King but also positioned it as a key player in the global fast-food industry, forcing competitors to rethink their strategies.
Burger King’s revival under 3G Capital demonstrates the power of focused leadership, disciplined financial management, and innovative marketing. It’s a textbook case of how a brand can be reinvented and reenergized through strategic clarity and bold execution.
Fast-Casual Restaurant Turnarounds: the Case of Chipotle
Chipotle’s turnaround is a remarkable example of crisis management and strategic recovery. After the devastating E. coli and norovirus outbreaks in 2015, which led to a significant loss in customer trust and a sharp decline in sales and stock price, Chipotle took several decisive actions to restore its reputation.
Key Actions:
- Leadership Change: In 2018, Brian Niccol, former CEO of Taco Bell, was brought in to lead the recovery. He emphasized improving food safety protocols, digital transformation, and marketing efforts to re-engage customers.
- Food Safety Overhaul: Chipotle implemented stringent food safety measures, including high-resolution testing of ingredients, enhanced employee training, and the establishment of a Food Safety Advisory Council to oversee operations.
- Digital Transformation: Chipotle invested heavily in digital channels, enhancing its app, online ordering system, and delivery services. This move was pivotal, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, as it helped the brand maintain and grow its customer base.
- Brand Repositioning: The company also refocused on its “Food with Integrity” philosophy, launching campaigns that highlighted its commitment to fresh, ethically sourced ingredients.
Results: These strategies led to a strong recovery, with Chipotle’s stock price rebounding and reaching new highs. The company’s emphasis on food safety, digital innovation, and transparent communication helped restore consumer trust and drive sustained growth
Chicken Restaurant Turnarounds: the Case of Popeyes’
Popeyes’ turnaround is an impressive example of how leadership, marketing innovation, and a strategic focus on franchisee relationships can revive a struggling brand. Here are the key strategies and results from Popeyes’ transformation:
- Leadership and Servant Leadership Approach:When Cheryl Bachelder took over as CEO in 2007, Popeyes was in decline. Bachelder implemented a leadership style rooted in servant leadership, focusing on supporting and empowering franchisees, who she viewed as the brand’s most important customers. She embarked on a “listening tour” to understand the challenges faced by franchisees and used this feedback to address the company’s most critical issues. This approach fostered stronger relationships with franchisees, who then became more invested in the brand’s success, leading to improved operational performance and increased profitability.
- Marketing and Product Innovation:Popeyes’ marketing strategy played a significant role in its resurgence. The brand leveraged social media effectively, particularly during the launch of its now-famous Chicken Sandwich in 2019. This launch not only went viral but also spurred immense customer engagement through user-generated content, memes, and discussions that spread across platforms like Twitter and Instagram. Popeyes’ innovative and culturally resonant advertising, which often used humor and pop culture references, further solidified its appeal, especially among younger consumers.
- Strategic Global Expansion:Popeyes also focused on thoughtful international expansion, partnering with experienced local franchisees to navigate cultural and market-specific challenges. This approach allowed Popeyes to tailor its offerings to regional tastes while maintaining its core brand identity. This global strategy has been key to Popeyes’ ambition to become a leading player in the global fried chicken market.
Results: These strategies yielded remarkable results. Under Bachelder’s leadership, Popeyes’ stock price rose from $13 per share to $79, and restaurant revenues grew by 45%, with bottom-line profits more than doubling. The brand has also expanded its global footprint, becoming a significant competitor in international markets.
Popeyes’ turnaround illustrates the power of strategic leadership, franchisee support, and innovative marketing in transforming a brand and driving sustained growth.
Burger Restaurant Turnarounds: the Case of Wendy’s
Wendy’s turnaround story is one of strategic shifts, digital transformation, and community engagement, which collectively helped the brand regain its footing in the competitive fast-food industry.
- Strategic Partnerships and Community Engagement:Wendy’s focused on deepening its connection with local communities through creative partnerships. For instance, in collaboration with the Boise Hawks, an independent baseball team, Wendy’s launched the “Boise Baconators” promotion, where the team temporarily rebranded itself after Wendy’s popular Baconator® sandwich. This initiative not only drove community engagement but also boosted sales and brand visibility. The campaign concluded with an auction of Baconator-themed gear, with proceeds benefiting the Dave Thomas Foundation for Adoption (DTFA), reinforcing Wendy’s commitment to social responsibility.
- Digital Transformation:In recent years, Wendy’s has significantly invested in digital transformation to modernize its operations and enhance customer experiences. The company has prioritized the integration of advanced technologies, including AI, big data, and mobile technologies, to streamline operations and personalize customer interactions. This digital focus also extends to Wendy’s marketing strategies, where the brand has effectively utilized social media platforms to engage with customers, drive traffic, and maintain a strong online presence.
- Brand Revitalization and Market Positioning:Throughout its turnaround, Wendy’s has continuously worked on brand revitalization, ensuring it remains relevant in a rapidly changing market. The company’s efforts to innovate its menu, coupled with clever marketing campaigns, have helped Wendy’s differentiate itself from competitors. These strategies, along with a strong emphasis on customer engagement and digital innovation, have positioned Wendy’s for sustained growth and increased market share.
Wendy’s turnaround demonstrates the power of combining strategic community initiatives, a focus on digital transformation, and effective marketing to revitalize a brand in a competitive industry.
Take Action Before It’s Too Late
In the high-stakes world of restaurant turnarounds, waiting too long to take action is costly. Whether you’re an investor looking to protect your capital or a business leader facing declining performance, a proactive approach is critical. At Aaron Allen & Associates, we have the expertise and experience to guide you through the turnaround process, helping you restore profitability, enhance operations, and position your business for long-term success.
A restaurant turnaround is like performing surgery on a business—it requires precision, careful diagnosis, and a clear plan for recovery. The anatomy of a successful turnaround typically follows a few critical phases.
First, you start with diagnostics. This is where you assess the situation in detail: financial health, operational inefficiencies, market positioning, and brand perception. It’s essential to understand the root causes of the challenges—whether it’s declining sales, high costs, poor customer satisfaction, or all of the above. Data collection and analysis are key here, as they will inform every subsequent step.
Next comes the design phase. Based on the diagnostics, you develop a strategic plan to address the identified issues. This often involves rethinking the menu, renegotiating with suppliers, optimizing labor costs, and refreshing the brand’s marketing approach. It might also mean overhauling management structures or even re-evaluating the restaurant’s location. The design phase is about setting the course for recovery, with clearly defined goals and milestones.
The third phase is deployment. This is where the rubber meets the road. The strategic plan is implemented, often with immediate changes to stop the bleeding—like cutting unprofitable menu items, reducing waste, or revamping customer service training. It’s also where longer-term initiatives start, such as marketing campaigns, menu redevelopment, or capital improvements.
Finally, there’s the debrief and refine phase. Once the plan is in motion, continuous monitoring is essential. The market and business conditions might change, so the plan needs to be adaptable. This phase involves reviewing performance data, making adjustments, and ensuring that the restaurant remains on a path to sustained profitability and growth.
FAQs: Restaurant Turnarounds & Transformation Initiatives
About Aaron Allen & Associates
Aaron Allen & Associates is a global restaurant consultancy specializing in brand strategy, turnarounds, and value enhancement. We have worked with a wide range of clients including multibillion-dollar chains, hotels, manufacturers, associations and prestigious private equity firms.
We help clients imagine, articulate, and realize a compelling vision of the future, align and cascade resources, and engage and enroll shareholders and stakeholders alike to develop multi-year roadmaps that bridge the gap between current-state conditions and future-state ambitions. Learn More.

